Home
About Radon Training Course
This course is designed to teach industry-accepted methods of inspecting and testing homes for radon using national standards of practice
Your journey begins with a thorough discussion of radon gas, its decay products, and a history of its discovery, its prevalence, and the health effects associated with exposure. You will then learn about testing methodologies, how to perform a test for radon, how to perform a visual inspection for conditions that are favorable for radon entry, and how to complete a professional radon inspection report. You will also be exposed to techniques for reducing radon levels, known as mitigation. In addition to technical skills, this course provides practical guidance for informing your clients of the presence of radon, along with other recommendations to ensure your testing and reporting achieves the highest standards of professionalism and accuracy.
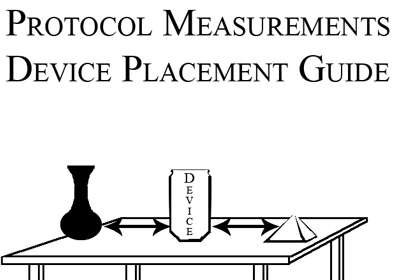
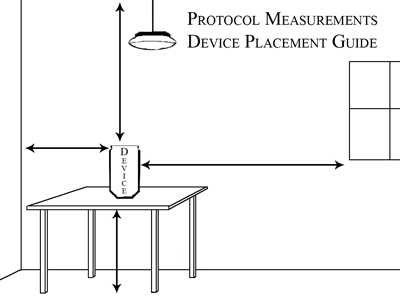
Learn about radon device placement and minimum measurement requirements to ensure the tests you run are always reliable.
Terminology
- Learn terms and definitions used in radon industry
- Learn terminology used for testing devices
- Understand how to communicate about radon measurement findings / results
Understanding Radon
- Define radon gas and describe its characteristics
- Identify the radioactive properties of radon including progeny, half-life and ionization
- Recognize the history of the discovery of radon
- Identify and describe the units of measurement used for radon
- Describe the relationship of uranium mining to radon exposure
- Define what is considered unsafe levels of radon
- Describe how radon can cause disease
- Identify the differences of radon in the air vs radon in water
- Demonstrate an understanding of cellular damage caused by ionizing radiation
- Identify the risks associated with smoking and radon exposure
- Identify the relative risk of radon exposure to that of other causes of death
Radon Testing
- Recognize the importance of certification and licensing requirements
- Describe the purpose of testing for radon
- Describe the protocol for real estate transaction testing
- Describe the importance of inspecting for entry points
- Identify proper test device locations
- Describe the differences in short-term vs long-term tests
- Define the term closed-house conditions
- Recognize the different methods of testing for radon
- Describe how to choose the appropriate testing method
- Describe how the time of year and the weather may affect testing
- Demonstrate how to take a water sample
Testing Devices
- Identify where to place radon test devices.
- Describe situations where additional test locations are encouraged.
- Know what can impact measurement, creating uncertainties.
- Describe how to perform a comparison check.
- Define counting efficiency and how it is used.
- Know testing tips for achieving valid radon measurements.
- Identify the reasons for radon testing.
- Know when to retest for radon.
- Describe passive radon testing and passive devices.
- Describe alpha track detectors, including the advantages and disadvantages of these devices.
- Describe activated charcoal devices, including the advantages and disadvantages of these devices, the diffusion barrier possibility along with possible corrections that may be needed.
- Describe charcoal liquid scintillation detectors, including the advantages and disadvantages of these devices.
- Describe electret ion chamber detectors, including the advantages and disadvantages of these devices.
- Describe active radon testing and active devices.
- Describe continuous radon monitoring devices (PMT, pulsed ion chamber, and solid state silicon detector), including their advantages and disadvantages.
- Describe the sniffing mode that comes with some continuous radon monitoring devices.
- Describe continuous working level devices, including the advantages and disadvantages.
- Describe the radon progeny integrating sampling unit.
- Explain the testing protocol and performance criteria for NRPP approved devices.
- Explain when to test water for radon.
- Know the recommendations for radon in drinking water.
- Describe radon transfer from water to air, and how it might impact radon testing.
- Know the role of advection, diffusion, and emanation in radon transportation.
- Know the recommendation for safe radon levels in drinking water.
- Describe how a home's radon level can be impacted by radon in water.
- Describe the process for testing water for radon.
- Describe the two methods for removing radon from water.
Results and Reporting
- Demonstrate how to ensure valid results through device handling and retrieval
- Describe how a chain of custody works to ensure valid results
- Define quality assurance
- Identify and describe the elements of a comprehensive QA document
- Define the term standard operating procedure
- Describe how quality control acts to ensure valid results and detects interference
- Identify the purpose of routine instrument performance checks
- Identify and describe the purpose and importance of duplicates, spikes and blanks in relation to QA
- Demonstrate an understanding of relative bias
- Demonstrate an understanding of precision and relative percent difference
- Identify the importance of control charts
- Describe methods of preventing and detecting interference
- Describe how weather conditions can affect radon concentration
- Identify the possible seasonal and diurnal variations in radon concentrations
- Understand the purpose and scope of a radon inspection report
- Demonstrate how to prepare a radon inspection report
- Identify the recommended components of radon level and test result reporting
- Describe how and when to use a mitigation system inspection checklist
- Describe how to submit your findings to your client, including how and when to suggest a retest or recommend mitigation
Mitigation
- Learn practices in installing radon reduction systems that meet industry standards.
- Know the minimum requirements for reducing soil gas entry into homes, for the purpose of reducing exposure.
- Know the general guidance for reducing soil gas entry.
- Know when current ANSI/AARST standards apply to previously installed mitigation systems.
- Know the importance of having a Quality Management System and Quality Control Procedures document.
- Know the best practices and expectations for communication with homeowners regarding radon exposure, radon test results, mitigation system proposal, mitigation system installation, and mitigation system operations, maintenance, and monitoring plans.
- Describe the notifications needed prior to installation of the mitigation system.
- Understand the importance of following all local building codes, including obtaining required permits/licenses.
- Know considerations for mitigation system design.
- Demonstrate knowledge of diagnostic investigation for effective mitigation system design.
- Describe the ASD mitigation process, including suction points, sumps, non-habitable air spaces, block walls, piping, exhaust discharge, protection from elements, and fan installation.
- Describe the purpose and process of sealing.
- Describe the OMM plan and its purpose.
- Know the requirements for system inspection post-installation.
- Demonstrate knowledge of purpose and extent of record keeping.
- Describe the process for post-mitigation testing.
- Describe the conditions under which additional mitigation testing (beyond the standard two year retest timeframe) should take place.
- Demonstrate knowledge of health and safety guidelines during mitigation work.
- Calculate WLM when provided with example data.
- Describe Non-ASD mitigation systems and when they might be used.
Course Review
Final Exam

 Your journey begins with a thorough discussion of radon gas, its decay products, and a history of its discovery, its prevalence, and the health effects associated with exposure. You will then learn about testing methodologies, how to perform a test for radon, how to perform a visual inspection for conditions that are favorable for radon entry, and how to complete a professional radon inspection report. You will also be exposed to techniques for reducing radon levels, known as mitigation. In addition to technical skills, this course provides practical guidance for informing your clients of the presence of radon, along with other recommendations to ensure your testing and reporting achieves the highest standards of professionalism and accuracy.
Your journey begins with a thorough discussion of radon gas, its decay products, and a history of its discovery, its prevalence, and the health effects associated with exposure. You will then learn about testing methodologies, how to perform a test for radon, how to perform a visual inspection for conditions that are favorable for radon entry, and how to complete a professional radon inspection report. You will also be exposed to techniques for reducing radon levels, known as mitigation. In addition to technical skills, this course provides practical guidance for informing your clients of the presence of radon, along with other recommendations to ensure your testing and reporting achieves the highest standards of professionalism and accuracy.
